Indigenous empowerment for climate-resilient solutions in Africa
At COP 28 side event Indigenous leaders discussed empowering Indigenous communities with financial resources and inclusive carbon markets to scale up climate solutions.
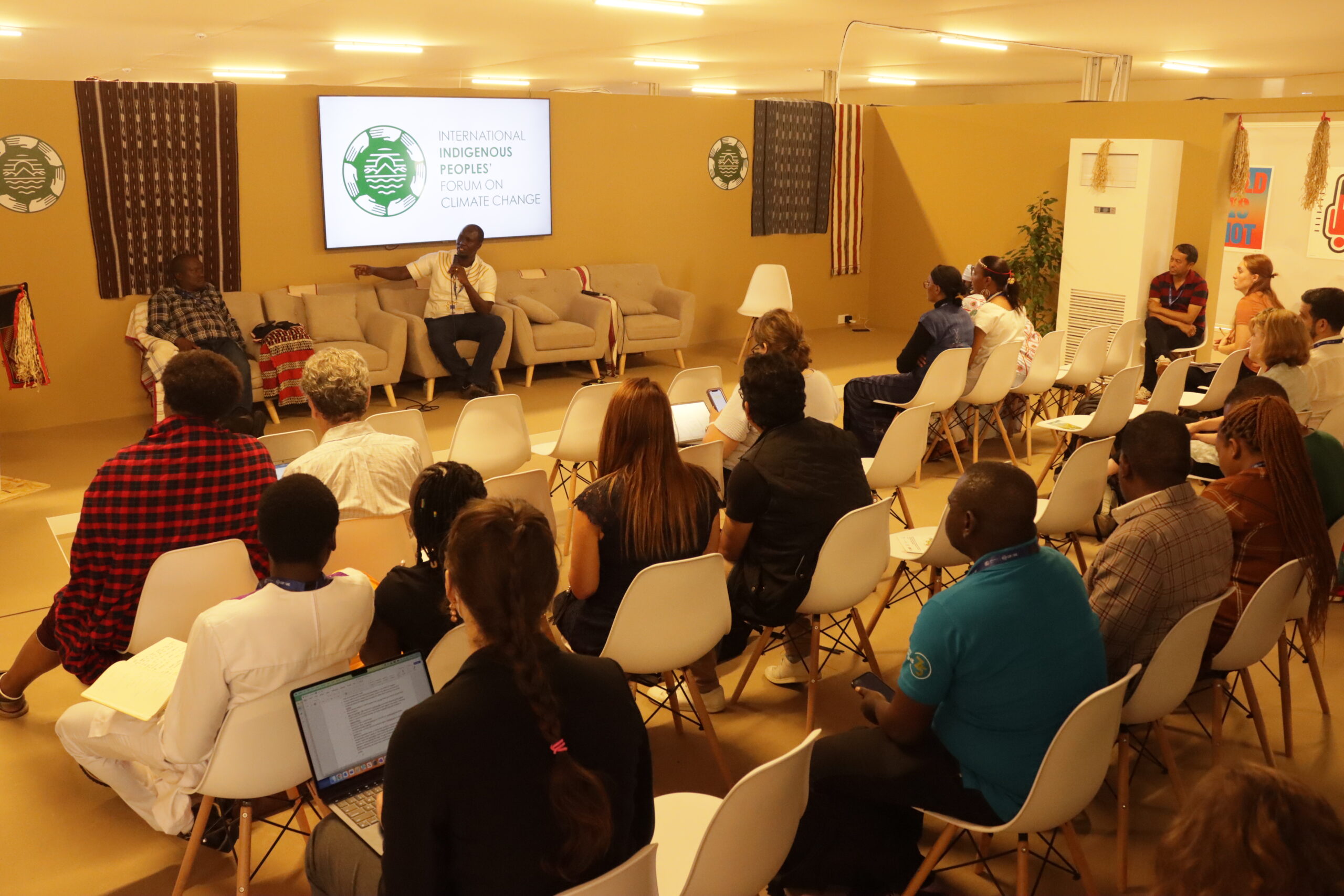

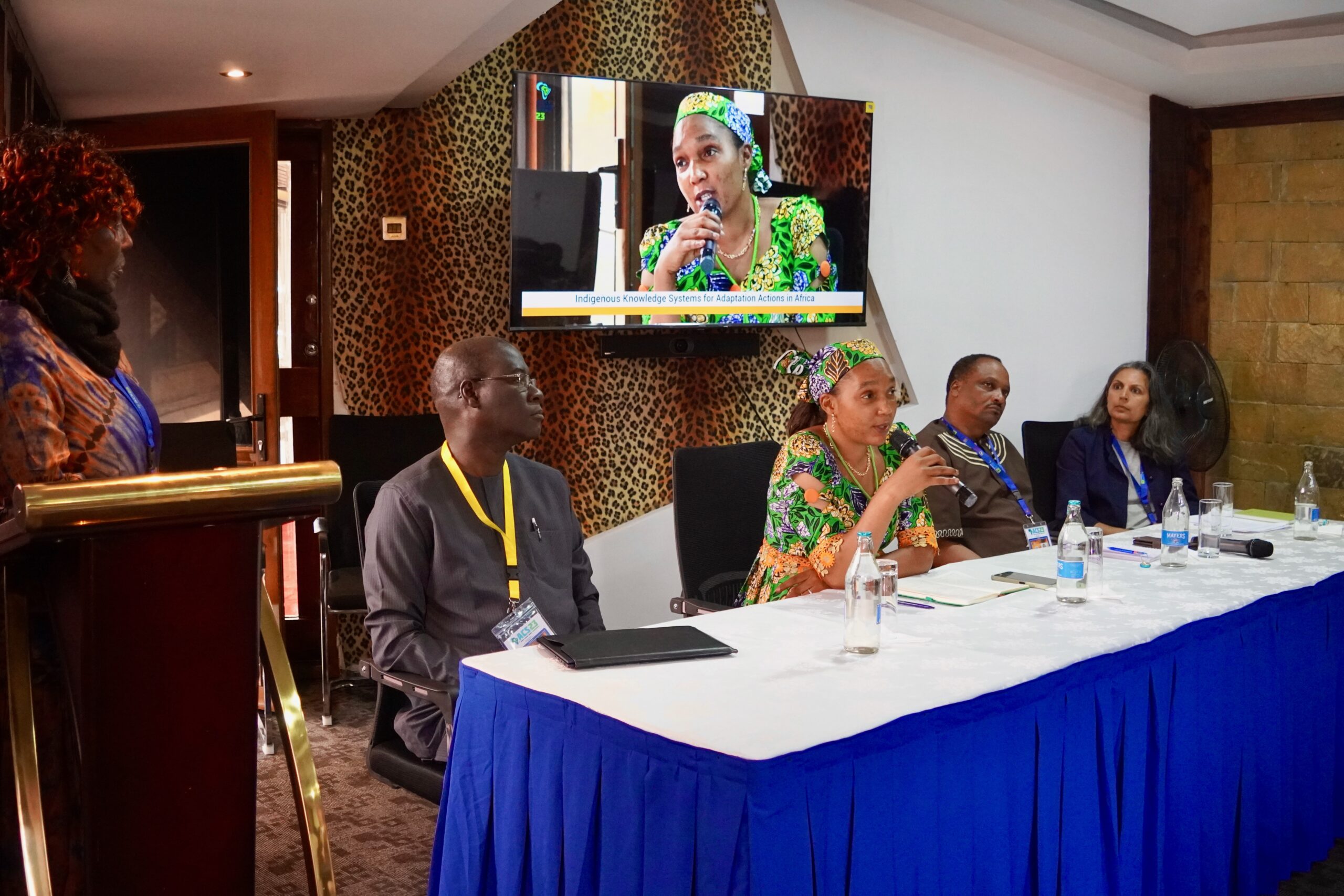
At COP 28, the FSC Indigenous Foundation, the Indigenous Peoples of Africa Coordinating Committee (IPACC), the United States Agency for International Development (USAID)’s Inclusive Development Hub convened experts at an event on December 5 in the Indigenous Peoples Pavilion, Engaging Indigenous Peoples in Carbon Markets: Direct access to climate finance for Indigenous communities in Africa to increase awareness of the unique contributions of Indigenous communities to climate resilience and to discuss opportunities, challenges and solutions related to direct climate finance and carbon markets.
The need for direct and inclusive mechanisms
The global challenges of biodiversity loss and climate change require urgent and collaborative action. Indigenous communities, often the stewards of rich biodiversity, possess unique knowledge and sustainable practices that can significantly contribute to climate resilience. By fostering direct access for Indigenous Peoples to climate finance, we can empower Indigenous communities in Africa to implement sustainable solutions, contributing significantly to the broader goals of biodiversity conservation and climate resilience.
Carbon markets could be a way of empowering Indigenous Peoples by paying them for protecting the world’s forests. Indigenous and community lands hold at least 22% of the carbon stored in tropical and subtropical forests globally. These markets have the potential to create a unique opportunity for Indigenous communities to develop an economic sector aligned with Indigenous lifestyles, Indigenous Cultural Landscapes, and sustainable land management. It is also an opportunity for governments and industry to co-create meaningful partnerships and develop relevant policies with Indigenous Peoples.
On the other hand, some Indigenous communities fear that further development of carbon markets, even with the new rules agreed to at COP 27, will endanger local livelihoods and create loopholes for further emissions. Markets must be designed in a transparent way that responds to the needs and realities of Indigenous communities.
Perspectives from Indigenous leaders
We took the opportunity of COP28 to create an inclusive space to identify the key constraints, challenges, and opportunities of climate finance and carbon markets.
To begin the event, Hindou Oumarou Ibrahim, FSC Indigenous Foundation Council Chair gave opening remarks.
“What is the carbon market, and how is it going to respect the land and rights of Indigenous Peoples?” she asked. “If governments are going engage in the carbon market, we are not going to let them do it without getting the benefit and we are not going to let them do it while harming our lives and our territories.”


A panel with Indigenous leaders and partner organizations shared perspectives and key insights on how we can engage stakeholders from the realms of climate finance, environmental policy, and Indigenous rights advocacy to ensure direct access to finance for Indigenous communities.
Panelists also discussed how Indigenous Peoples can benefit from carbon markets, and which concerns need to be addressed for more Indigenous Peoples to participate.
“There is a big debate that carbon is a false solution”, said Kanyinke Sena, Executive Director of IPACC. “We must understand that carbon in itself is not a bad thing, what is a bad thing is the people that use that to come and benefit – the carbon cowboys.”
He also emphasized the importance of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) for communities engaging in the carbon market.
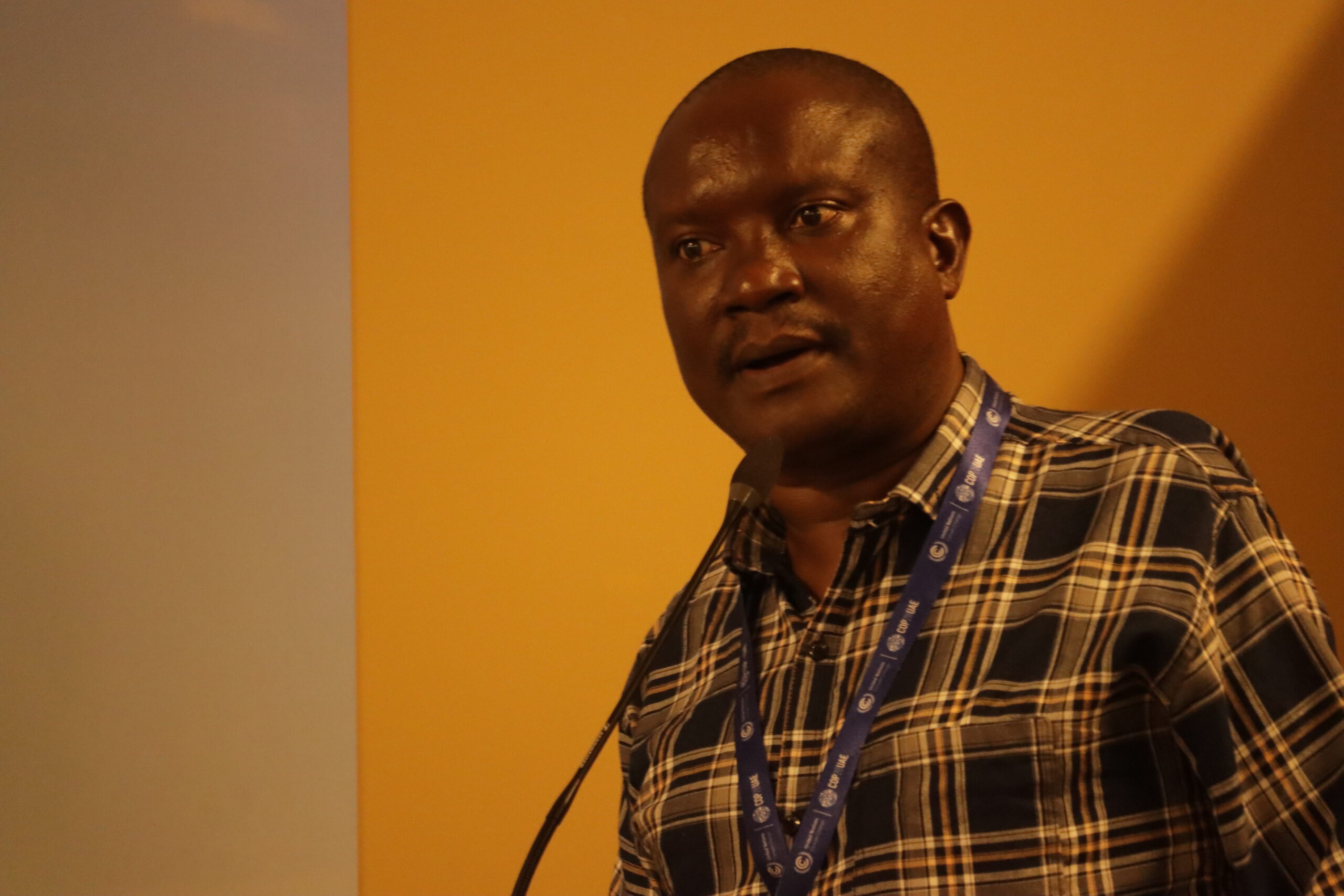
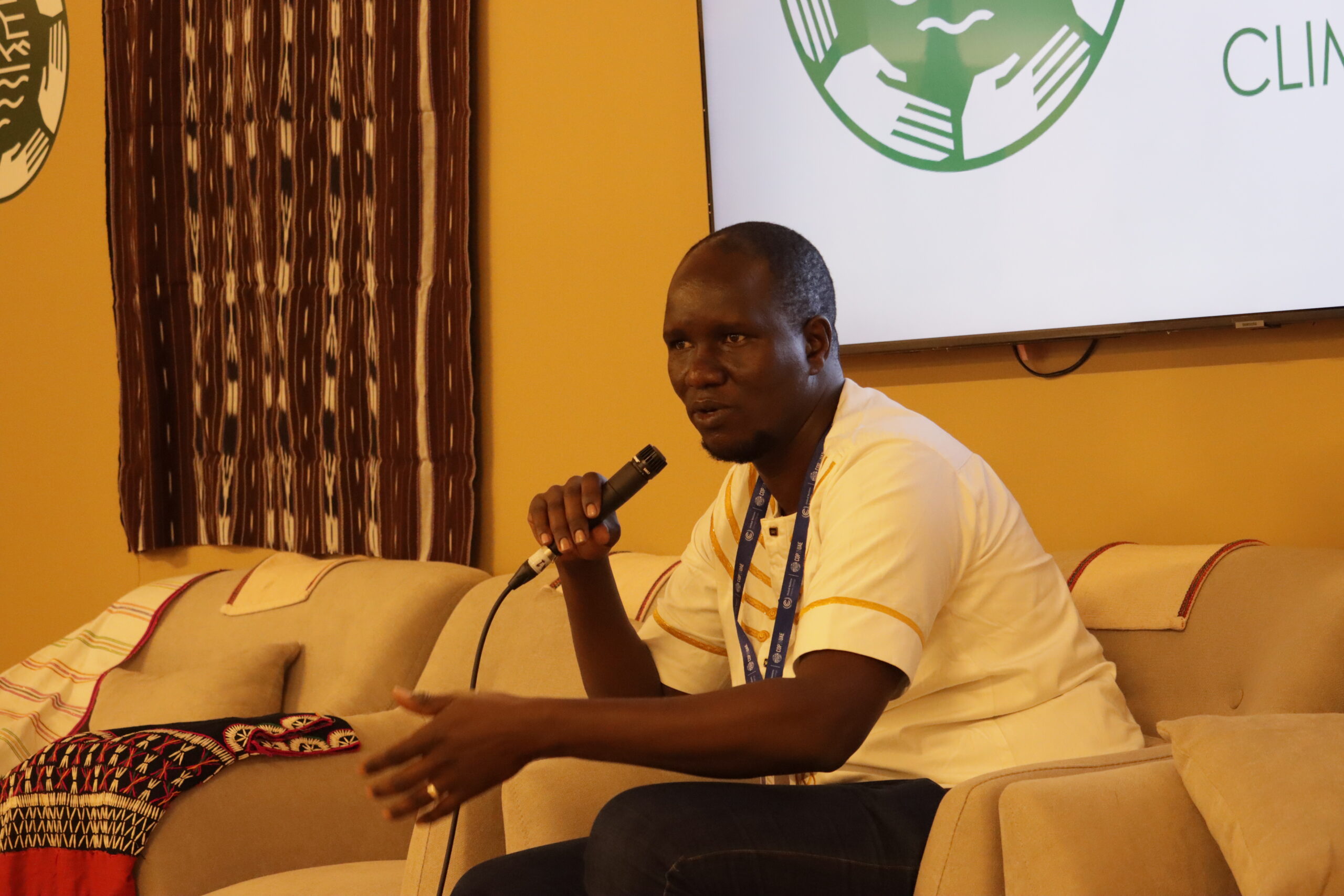


Elijah Toirai, Natural Climate Solutions (NCS) and Communities Lead at Conservation International discussed registration for carbon credits and the importance of carbon market reports remaining public. “We are seeing a shift towards Indigenous Peoples communities becoming the carbon credit entity. The Indigenous Peoples’ communities and organizations are registering the projects. That way, when it comes to benefit sharing, the buyers actually then pay to these Indigenous Peoples’ organizations,” he said.
Joseph Itongwa, Coordinator of REPALEAC and IPACC Great Lakes representative, posed an important question: “Where can we report the wrongdoers in the carbon credit equation?”
The question and answer section presented the opportunity to exchange knowledge and information from other regions.
“We, the Indigenous Peoples, have organized ourselves and have proposed our own climate strategy, called the Amazon Indigenous Network, in the face of this challenge. We are looking for the rights of Indigenous Peoples to come first, and the right of access to the territories. We are implementing REDD (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation) with the guidelines of the Amazon Indigenous Network,” said Fermín Chimatani Tayori of the National Association of Contract Executors for the Administration of Communal Reserves of Peru.


Panelists concluded that it is vital to ensure the respect of Indigenous Peoples’ rights in the development of carbon markets. Indigenous Peoples need to be included in the design of these mechanisms so they can engage in carbon markets, if they so choose, in favor of their communities, landscapes, and cosmovision.